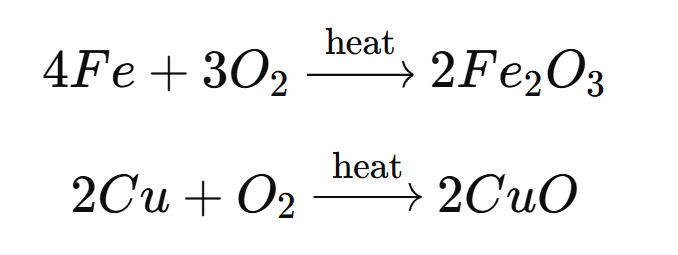1. Heating of Copper (Cu) in the Presence of Oxygen:
When copper is heated in the presence of oxygen, it forms copper(II) oxide.
2Cu + O₂ → 2CuO
2. Heating of Iron (Fe) in the Presence of Oxygen:
When iron is heated in the presence of oxygen, it forms iron(III) oxide.
4Fe + 3O₂ → 2Fe₂O₃
Combine Reactions
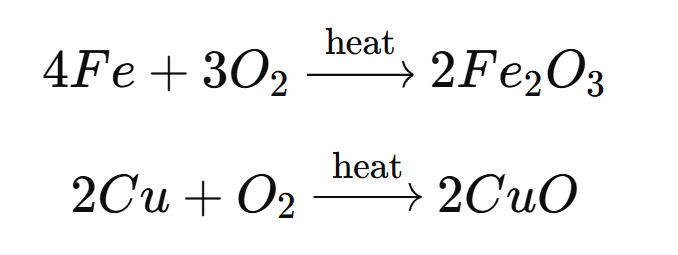
Copper (Cu) 🆚 Iron (Fe)

| Feature | Copper (Cu) | Iron (Fe) |
| Atomic Number | 29 | 26 |
| Symbol | Cu | Fe |
| Color | Reddish-brown | Silvery-gray |
| Density | 8.96 g/cm³ | 7.87 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 1,085°C (1,984°F) | 1,538°C (2,800°F) |
| Electrical Conductivity | Very high, second only to silver | Good, but less than copper |
| Corrosion Resistance | Highly resistant to corrosion | Prone to rusting when exposed to moisture and oxygen |
| Common Uses | Electrical wiring, plumbing, coins, electronics | Construction (steel), automotive, machinery |
| Occurrence | Found in native form and as ores like chalcopyrite | Found as ores like hematite and magnetite |
| Reactivity | Relatively low; reacts slowly with air to form a patina (green layer) | Reacts readily with oxygen and water, forming rust (iron oxide) |
| Alloys | Used to make brass (with zinc) and bronze (with tin) | Used to make steel (with carbon) and stainless steel (with chromium) |
FAQs
➡️ When copper (Cu) is heated in the presence of oxygen, it forms copper(II) oxide (CuO), a black solid. The reaction is: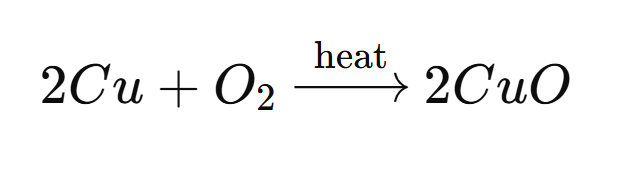
➡️ Iron reacts with oxygen at high temperatures to form iron(III) oxide (Fe₂O₃), which is reddish-brown in color.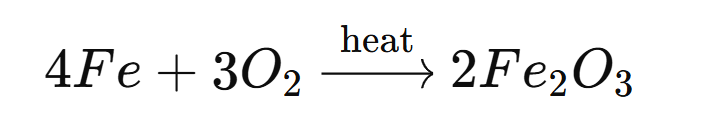
➡️ Fe₂O₃ (Iron(III) oxide) – Forms when iron burns in excess oxygen, appearing reddish-brown (rust).
➡️ Fe₃O₄ (Iron(II,III) oxide) – Forms at very high temperatures, appearing black (magnetite).
➡️ Yes, but very slowly. Copper forms a greenish patina (CuCO₃·Cu(OH)₂) over time. Iron undergoes rusting (Fe₂O₃·xH₂O) in the presence of moisture and oxygen.
➡️ Copper forms a simple oxide layer (CuO, black in color), while iron reacts with oxygen to form Fe₂O₃, which absorbs moisture and leads to rusting.
➡️ When heated in the presence of oxygen (O₂), copper (Cu) forms black copper(II) oxide (CuO), and iron (Fe) forms reddish-brown iron(III) oxide (Fe₂O₃).
➡️ This is an oxidation reaction, where both metals react with oxygen to form their respective oxides.