Ethanoic acid is called “glacial acetic acid” when it is in its pure, anhydrous form (without water). The term “glacial” comes from the fact that pure acetic acid solidifies just below room temperature, at 16.6°C (61.9°F), forming ice-like crystals that resemble a glacier.
Chemical Equation for Esterification:
Esterification is a reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol to form an ester and water. Alcohol + Carboxylic acid ⇌ Ester + Water
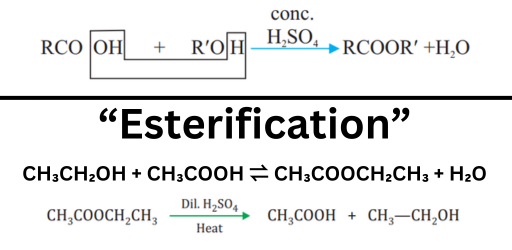
For ethanoic acid reacting with ethanol:
- CH₃COOH: Ethanoic acid (acetic acid)
- C₂H₅OH: Ethanol
- CH₃COOC₂H₅: Ethyl ethanoate (an ester)
- H₂O: Water
The reaction is typically catalyzed by concentrated sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄).
Related Questions:
A: The chemical equation for Fischer esterification is:
RCOOH + R’OH → RCOOR’ + H₂O
In this reaction, a carboxylic acid (RCOOH) reacts with an alcohol (R’OH) in the presence of an acid catalyst to produce an ester (RCOOR’) and water.
A: The esterification reaction mechanism involves these key steps:
Protonation of the carbonyl oxygen of the carboxylic acid by an acid catalyst, increasing electrophilicity.
Nucleophilic attack by the alcohol on the carbonyl carbon, forming a tetrahedral intermediate.
Proton transfers within the intermediate, leading to the elimination of water and the formation of the ester.
A: One example is the reaction between acetic acid (CH₃COOH) and ethanol (C₂H₅OH):
CH₃COOH + C₂H₅OH → CH₃COOC₂H₅ + H₂O
This produces ethyl acetate (CH₃COOC₂H₅) and water.
A: The esterification of acetic acid with ethanol can be represented as:
CH₃COOH + C₂H₅OH → CH₃COOC₂H₅ + H₂O
A: Esterification is the reaction of a carboxylic acid with an alcohol to form an ester and water:
RCOOH + R’OH → RCOOR’ + H₂O
A:
Esterification:
RCOOH + R’OH → RCOOR’ + H₂O
A carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol to form an ester.
Saponification:
RCOOR’ + NaOH → RCOONa + R’OH
An ester reacts with a strong base to form a carboxylate salt and alcohol.
A: The balanced equation for the Fischer esterification forming ethyl ethanoate is:
CH₃COOH + C₂H₅OH → CH₃COOC₂H₅ + H₂O
A: A generic balanced equation is:
RCOOH + R’OH → RCOOR’ + H₂O
Example with acetic acid and ethanol:
CH₃COOH + C₂H₅OH → CH₃COOC₂H₅ + H₂O
A: The general chemical formula for esters is:
RCOOR’, where R is the alkyl or aryl group from the carboxylic acid, and R’ is the alkyl or aryl group from the alcohol.
A:
Esterification:
RCOOH + R’OH → RCOOR’ + H₂O
Saponification:
RCOOR’ + NaOH → RCOONa + R’OH
A: A generic balanced equation for Fischer esterification is:
RCOOH + R’OH → RCOOR’ + H₂O
For ethyl acetate:
CH₃COOH + C₂H₅OH → CH₃COOC₂H₅ + H₂O
