Cells were first discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665. He observed thin slices of cork under a microscope and noted that they were made up of tiny compartments resembling the cells (rooms) of a monastery, hence the term “cell.”
What is a Cell?
Cell is the basic unit of life. All living things are made up of cells. Cells can be either single-celled organisms, such as bacteria, or they can be part of multicellular organisms, such as humans.
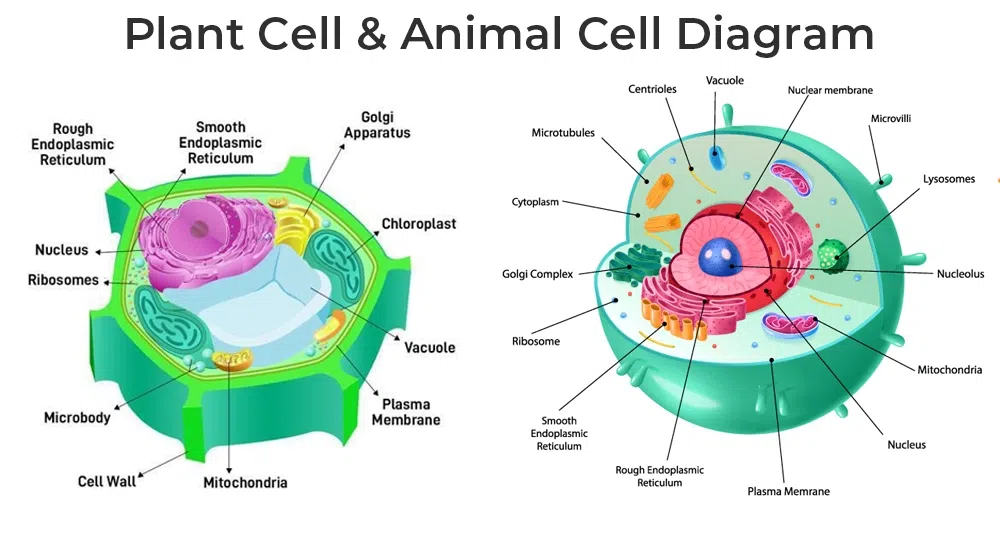
Types of cell
- Prokaryotic cells are the simplest type of cell. They have no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotic cells include bacteria and archaea.
- Eukaryotic cells are more complex than prokaryotic cells. They have a nucleus that contains the cell’s genetic material, as well as membrane-bound organelles that carry out specific functions. Eukaryotic cells include animal cells, plant cells, and fungal cells.

Timeline of Cell Discovery & Major Developments
FAQs
🔹 The plasma membrane protects the cell, controls the entry and exit of substances, and helps in cell communication.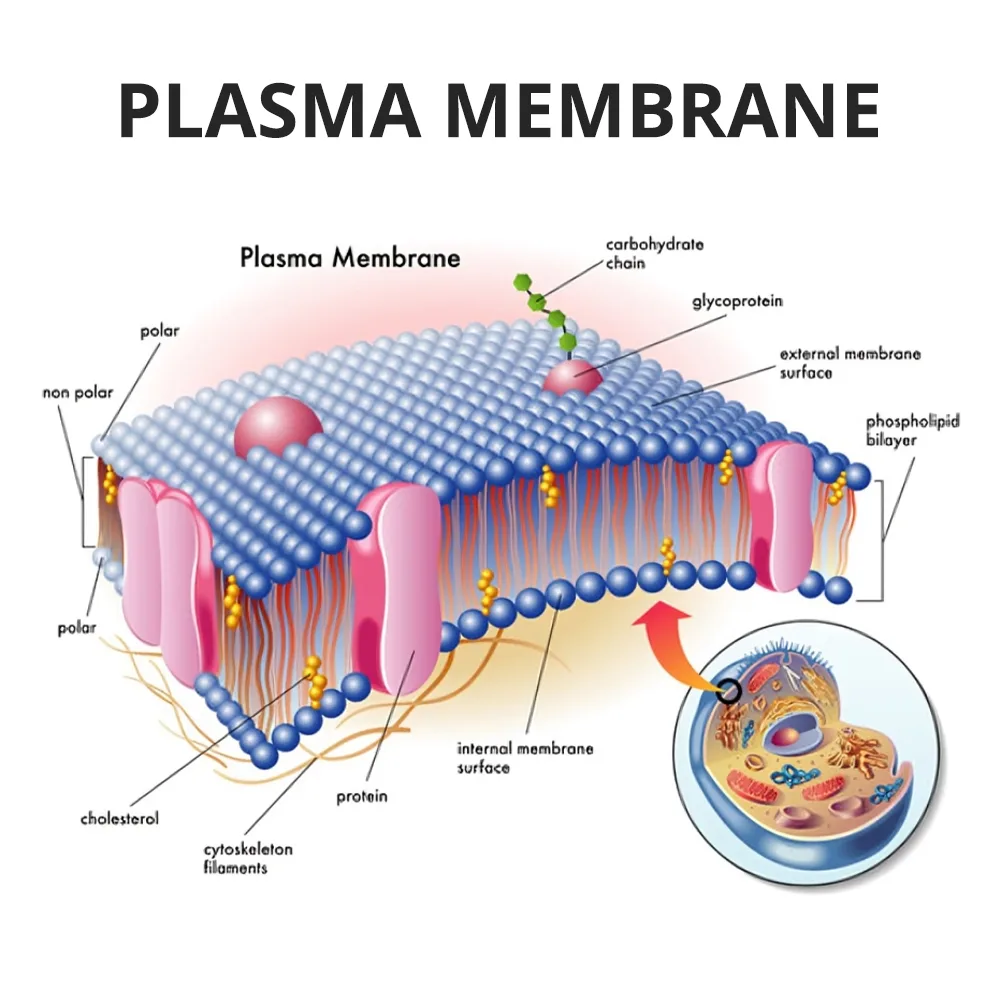
🔹 It regulates the movement of water, ions, and nutrients, ensuring a stable internal environment.
🔹 Membrane proteins help in transport, cell recognition, enzyme activity, and signal transmission.
🔹 It allows water molecules to move in and out, balancing the concentration of solutes inside and outside the cell.
🔹 The cell loses its selective permeability, leading to uncontrolled exchange of substances, which can cause cell damage or death.
