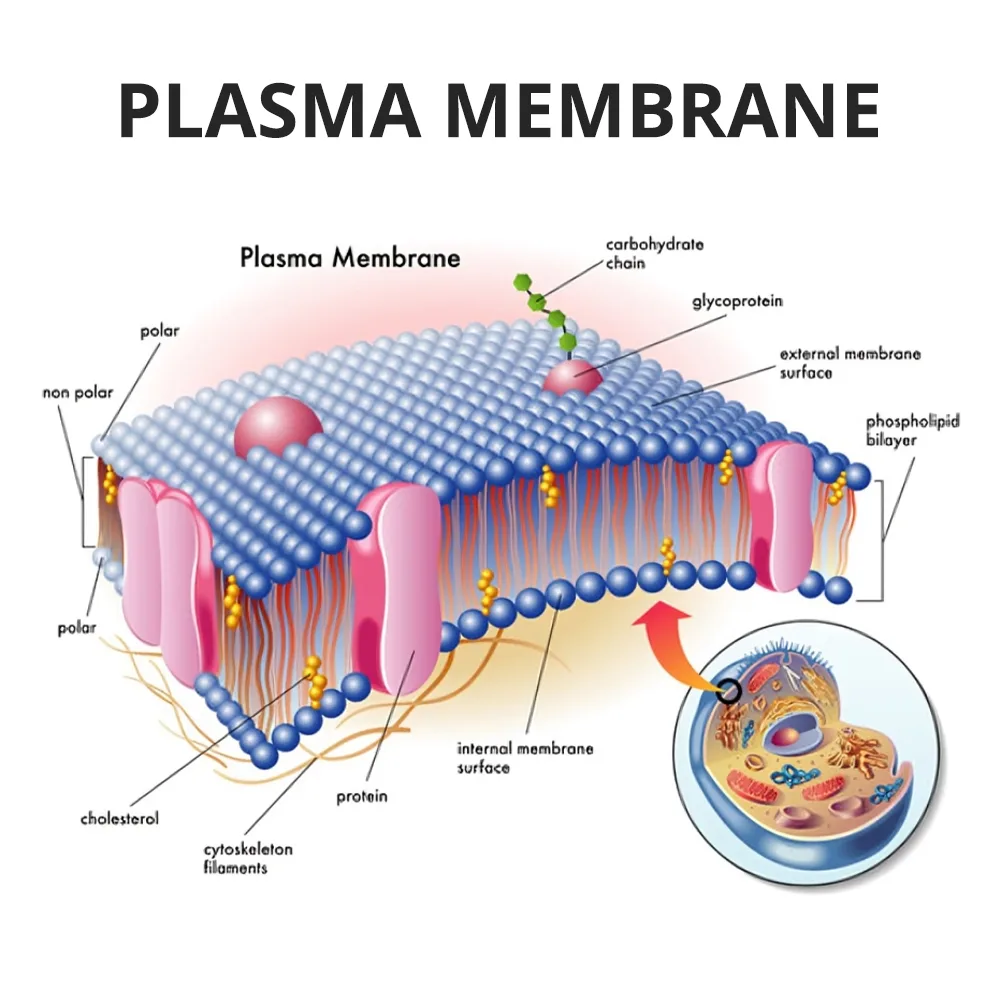
Plasma Membrane Rupture: A broken plasma membrane is catastrophic (आपत्तिजनक) for the cell. It acts as a barrier, controlling what enters and leaves the cell. A rupture disrupts this control, leading to uncontrolled movement of molecules and ions, causing the cell to swell and burst, ultimately resulting in cell death.
Reason for Plasma Membrane Rupture
Plasma membrane rupture can occur due to various reasons:
- Physical Damage: External forces such as mechanical trauma, shear stress, or pressure can cause the membrane to rupture.
- Chemical Damage: Exposure to toxins, solvents, or chemicals can disrupt the integrity of the membrane, leading to rupture.
- Osmotic Shock: Sudden changes in osmotic pressure, such as rapid swelling or shrinkage of the cell, can exceed the membrane’s capacity, causing it to rupture.
- Pathogens: Some pathogens, like certain viruses or bacteria, can produce proteins or enzymes that disrupt the plasma membrane, leading to its rupture.
- Underlying Conditions: Conditions like inflammation, cell aging, or genetic disorders can weaken the membrane, making it more susceptible to rupture.
Overall, plasma membrane rupture compromises the cell’s integrity and can lead to cell death or dysfunction.