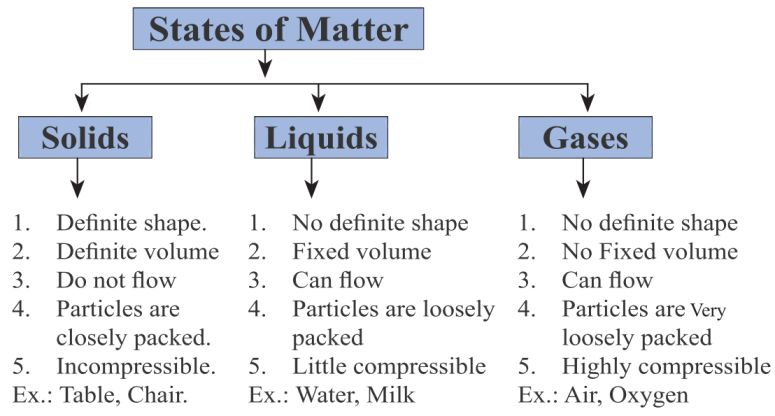
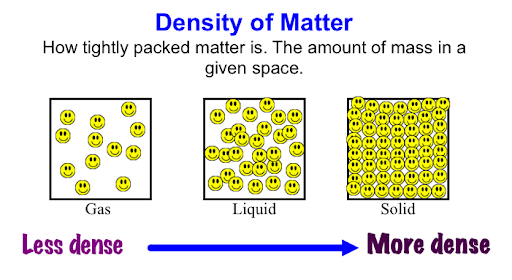
The melting point of ice is 0°C (32°F) at standard atmospheric pressure (1 atm).

However, this temperature can change under different pressures:
- Higher pressure can lower the melting point slightly.
- Lower pressure (like in high-altitude areas) can raise the melting point slightly.
But under normal conditions, ice melts at 0°C (32°F). ❄️
Frequently asked questions
→ At 0°C (32°F), ice absorbs heat and overcomes intermolecular forces, changing from solid to liquid (water).
→ Yes, if salt or other impurities are added, the melting point drops, which is why salt is used to melt ice on roads in winter.
→ Yes, higher pressure can lower the melting point slightly, while lower pressure can increase it.
→ Ice absorbs heat from its surroundings (including your hand) as it melts, making it feel cold.
→ It continues to melt into liquid water, and if heated further to 100°C (212°F), it turns into steam.