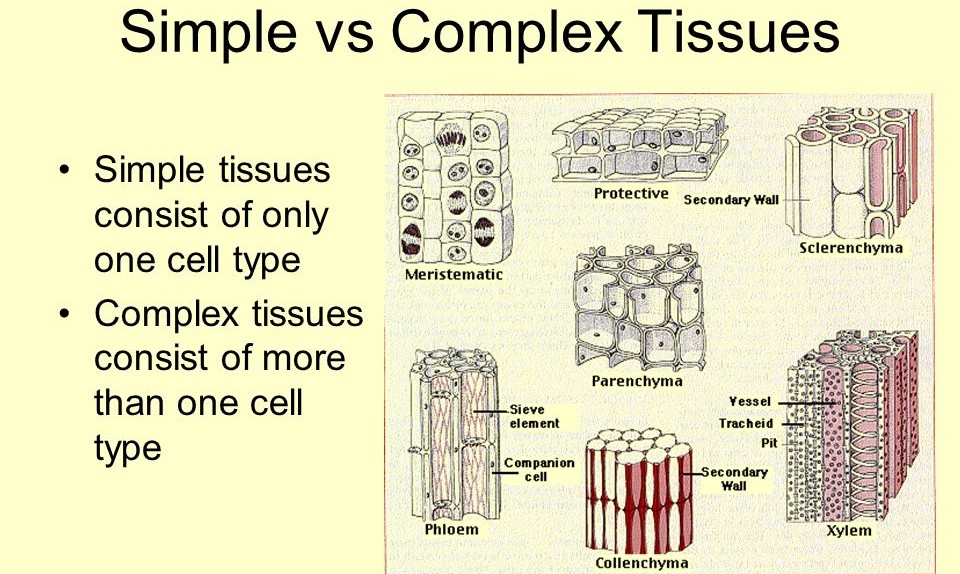
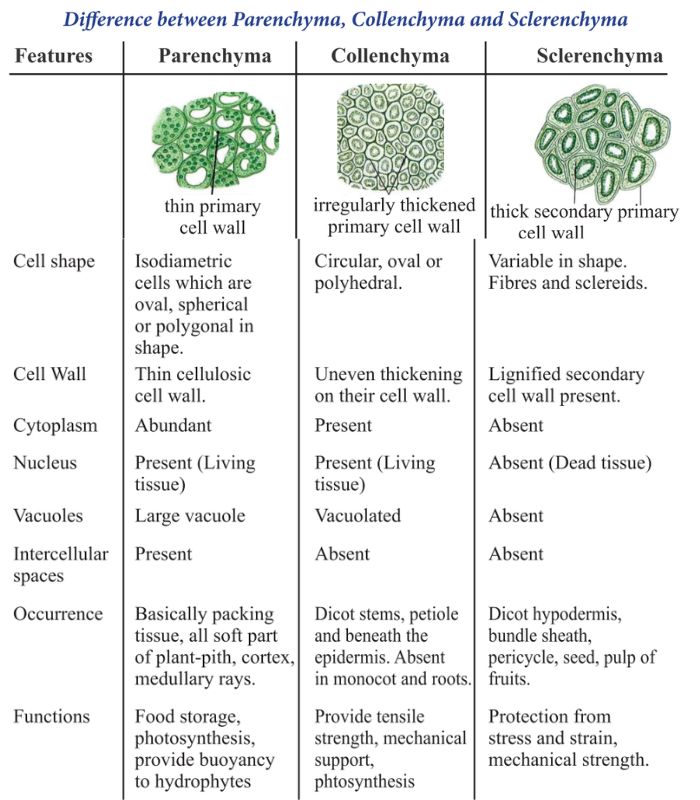
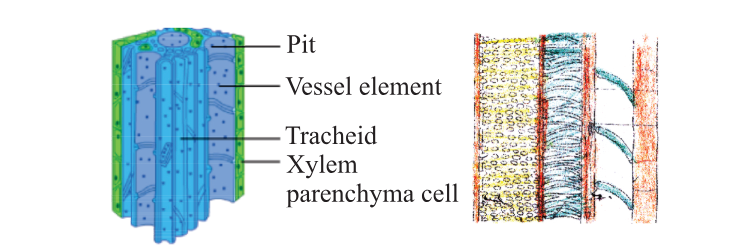
A tissue is a group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function. These cells share a common structure and origin, and they are organized in a way that allows them to efficiently carry out their specialized task.
Types of Tissue
Epithelial Tissue: This type of tissue covers the surfaces of the body and lines its organs and cavities. It provides protection, secretion, and absorption.
Connective Tissue: This type of tissue provides support, structure, and connects different parts of the body. It also stores fat and helps defend the body against disease.
- Bone Tissue: Provides support and structure for the body.
- Cartilage Tissue: Provides support and flexibility to structures like the joints.
- Blood Tissue: Transports oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body.
- Adipose Tissue (Fat): Stores energy and insulates the body.
- Fibrous Tissue: Provides support and structure to organs and other tissues
Muscle Tissue: This type of tissue allows the body to move. It is found in muscles that are attached to bones (skeletal muscle), within organs (smooth muscle), and in the walls of blood vessels (cardiac muscle).
- Smooth Muscle: Found in the walls of organs and blood vessels and allows for involuntary movement.
- Cardiac Muscle: Found in the heart and allows for the rhythmic contractions that pump blood throughout the body.
Nervous Tissue: This type of tissue is responsible for carrying messages throughout the body. It is found in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
- Neurons: Nerve cells that transmit messages throughout the body.
- Glial Cells: Support and protect neurons.