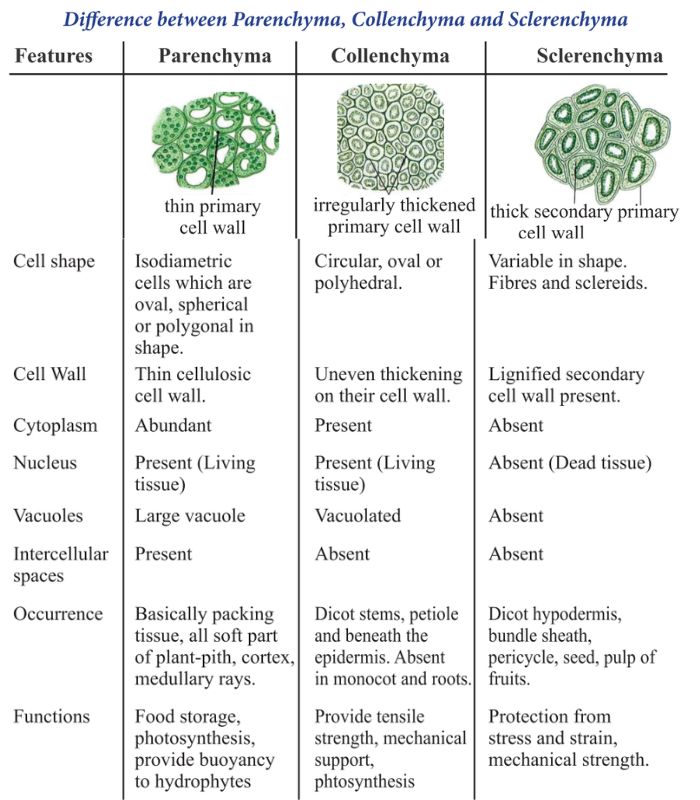
Xylem tissue consists of four types of cells:
- Tracheids – Long, tube-like cells that help in water conduction.
- Vessels – Large, hollow structures that transport water efficiently.
- Xylem Parenchyma – Stores nutrients and helps in transport.
- Xylem Fibers – Provide mechanical support to the plant.
Related FAQs
🔹 Xylem is responsible for transporting water and minerals from the roots to different parts of the plant and also provides structural support.
🔹 Xylem consists of four types of cells:
✅ Tracheids – Long, tube-like cells for water conduction.
✅ Vessels – Wider tubes that efficiently transport water.
✅ Xylem fibers – Provide mechanical support.
✅ Xylem parenchyma – Stores food and helps in transport.
🔹 Water moves upward through transpiration pull, root pressure, capillary action, and cohesion-tension forces in the xylem.
🔹 Most of the xylem (tracheids, vessels, and fibers) are dead at maturity, making them efficient for water conduction. Only xylem parenchyma is living and helps in storage.
🔹 Xylem transports water and minerals from roots to leaves (unidirectional).
🔹 Phloem transports food (sugar and nutrients) from leaves to other parts (bidirectional).