Detailed explanation with ray diagrams for images formed by a concave mirror for various object positions:
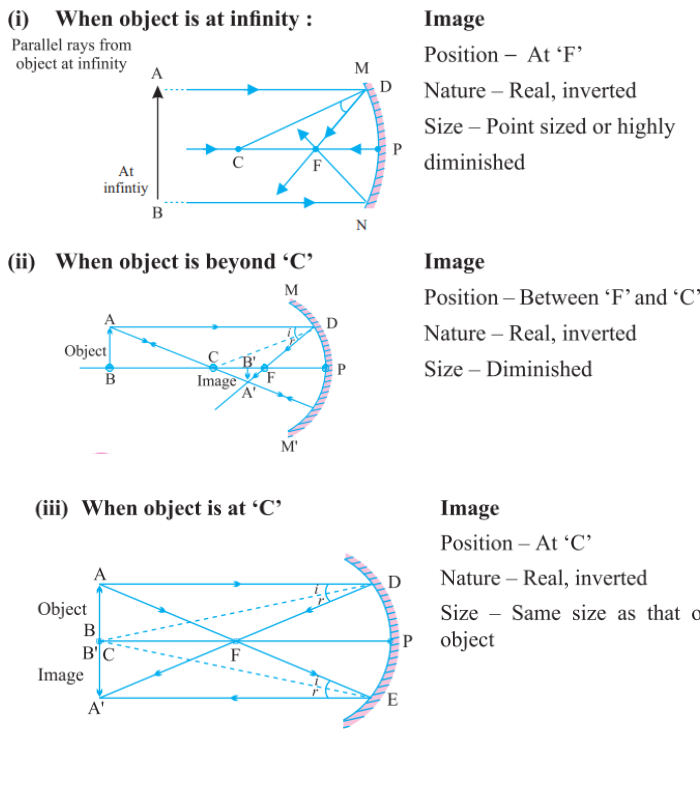
1️⃣ When the object is at infinity
- Ray Diagram: Parallel rays from the object reflect and converge at the principal focus (F).
- Image Position: At F.
- Nature: Real and inverted.
- Size: Point-sized (highly diminished).
2️⃣ When the object is beyond C
- Ray Diagram:
- One ray parallel to the principal axis reflects through F.
- Another ray passing through F reflects parallel to the principal axis.
- Image Position: Between F and C.
- Nature: Real and inverted.
- Size: Diminished (smaller than the object).
3️⃣ When the object is at C
- Ray Diagram:
- One ray parallel to the principal axis reflects through F.
- Another ray passing through the center of curvature (C) reflects back on the same path.
- Image Position: At C.
- Nature: Real and inverted.
- Size: Same size as the object.
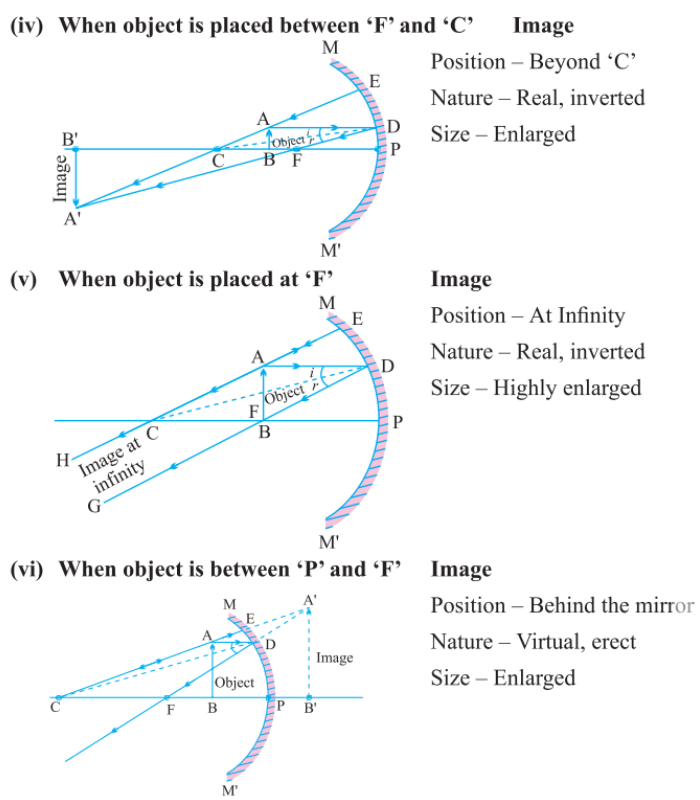
4️⃣ When the object is between C and F
- Ray Diagram:
- One ray parallel to the principal axis reflects through F.
- Another ray passing through C reflects back along its path.
- Image Position: Beyond C.
- Nature: Real and inverted.
- Size: Enlarged (larger than the object).
5️⃣ When the object is at F
- Ray Diagram:
- Rays from the object reflect in such a way that they become parallel after reflection.
- Since the reflected rays do not converge, the image forms at infinity.
- Image Position: At infinity.
- Nature: Real and inverted.
- Size: Highly enlarged.
6️⃣ When the object is between F and P (Pole)
- Ray Diagram:
- One ray parallel to the principal axis reflects through F.
- Another ray directed towards the center of curvature reflects back.
- Image Position: Behind the mirror.
- Nature: Virtual and upright.
- Size: Enlarged.
💡 Key Points for All Ray Diagrams:
- Use at least two principal rays for accuracy.
- The principal axis, focus (F), and center of curvature (C) are essential reference points.
- The laws of reflection guide how rays reflect on the mirror surface.
These detailed explanations can help visualize the image formation in a concave mirror!
