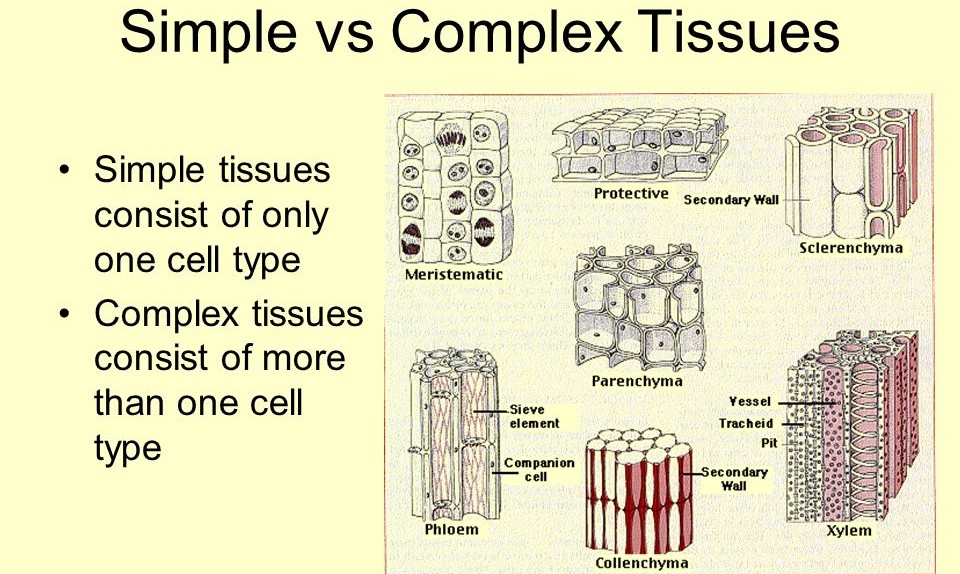
Simple tissues are composed of similar types of cells that perform a common function, while complex tissues are composed of different types of cells that work together to perform specialized functions.
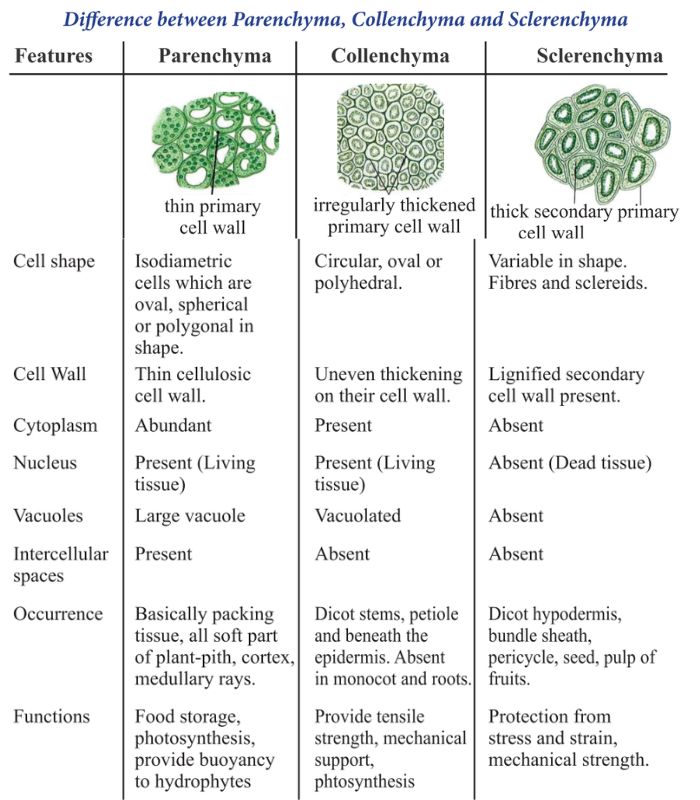
| Feature | Simple Tissues | Complex Tissues |
|---|---|---|
| Made of | One type of cell | More than one type of cell |
| Function | Support, storage, and photosynthesis | Transport of water, minerals, and food |
| Examples | Parenchyma (soft & stores food), Collenchyma (flexible support), Sclerenchyma (hard & strong) | Xylem (carries water), Phloem (carries food) |
| Living/Dead | Can be living or dead | Has both living and dead cells |
| Specialization | Less specialized | Highly specialized for transport |
| Found in | Stems, roots, and leaves | Vascular bundles (throughout the plant) |
Related FAQs
🔹 Simple tissues are made up of only one type of cell, while complex tissues consist of more than one type of cell working together for a common function.
🔹 Simple tissues include:
✅ Parenchyma – Soft, living cells for storage and photosynthesis.
✅ Collenchyma – Provides flexibility and mechanical support.
✅ Sclerenchyma – Dead, thick-walled cells for rigidity and strength.
🔹 Complex tissues include:
✅ Xylem – Transports water and minerals from roots to leaves.
✅ Phloem – Transports food (sugars and nutrients) from leaves to other parts of the plant.
🔹 Parenchyma (chlorenchyma) contains chloroplasts and helps in photosynthesis.
🔹 Xylem helps in water conduction, supporting plant hydration.
🔹 Phloem distributes nutrients, ensuring proper growth and energy supply.
🔹 Complex tissues perform specialized transport functions, unlike simple tissues that mainly provide support, storage, or photosynthesis. They help plants grow tall and transport materials efficiently.