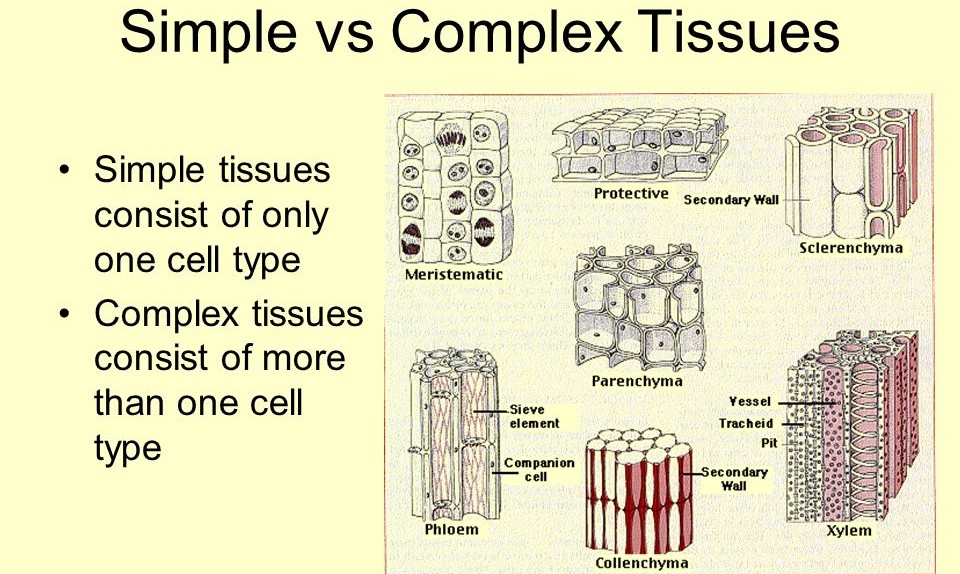
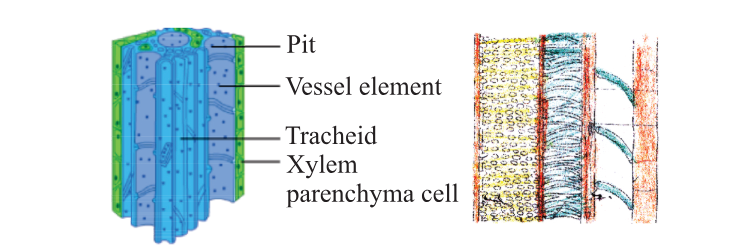
- Parenchyma: Cells have thin primary cell walls and may contain chloroplasts. They are involved in photosynthesis, storage, and secretion.
- Collenchyma: Cells have unevenly thickened primary cell walls, providing flexible support to young plant parts.
- Sclerenchyma: Cells have thick secondary cell walls strengthened with lignin, providing rigid support to mature plant parts.
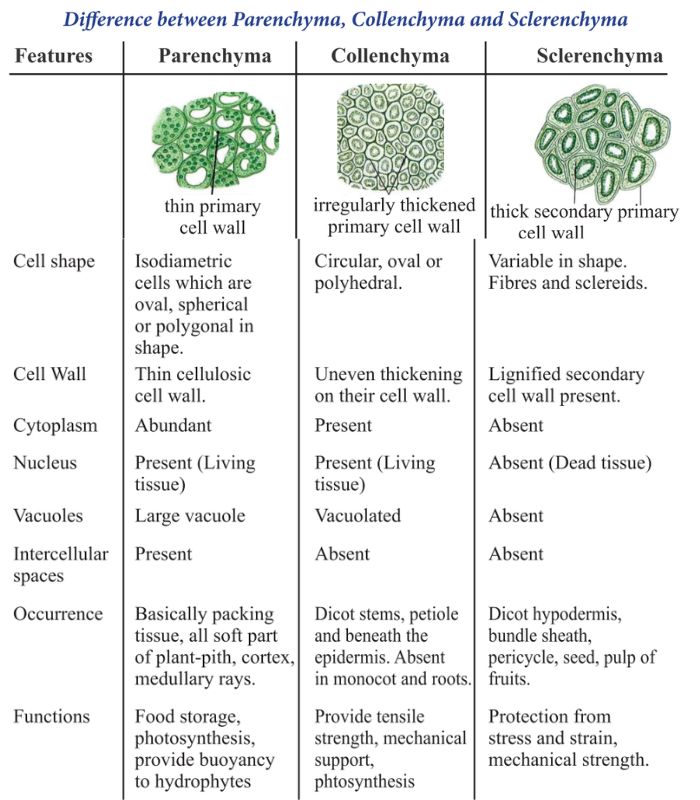
Differentiate between parenchyma collenchyma and sclerenchyma
| Feature | Parenchyma 🌿 | Collenchyma 🌱 | Sclerenchyma 🌳 |
| Composition | Primary cell wall made of cellulose | Primary cell wall with uneven thickenings of pectin and cellulose | Secondary cell wall with lignin deposition 🔗 |
| Thickness | Thin and uniform | Thickened at corners or unevenly | Thick and uniformly rigid |
| Flexibility | Flexible, allowing easy bending | Moderately flexible | Inflexible and rigid |
| Function | Provides support, storage, and photosynthesis | Provides mechanical support and flexibility | Provides maximum mechanical strength |
Frequently Asked Questions – Parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma
Parenchyma has thin walls, collenchyma has unevenly thickened walls, and sclerenchyma has thick, lignified walls.
Collenchyma provides flexibility, allowing plants to bend without breaking.
Collenchyma is typically found in young stems, petioles, and leaf veins where flexible support is needed.
Parenchyma cells are involved in photosynthesis, respiration, and storage of food and water.
Parenchyma cells, especially in leaves, have large intercellular spaces that facilitate gas exchange during photosynthesis.